The most unfortunate aspect of pregnancies is that they come with massive risks that can severely impact both the fetus and the mother. One of these risks includes the probability that the pregnancy you have may be ectopic.
An ectopic pregnancy is a high-risk pregnancy in which the fertilized egg is implanted anywhere other than the main cavity of the uterus, where it should be. The egg continues to grow wherever it is implanted, but it will not develop into a baby. Rather the mother will be at risk if such a pregnancy is to continue. Hence, it is best to remove it using medicines or a surgery.
This article will look more into an ectopic pregnancy, its symptoms, and preventive measures. It will also discuss the aftermath of ectopic pregnancy and how they can be dealt with.
What Happens in an Ectopic Pregnancy
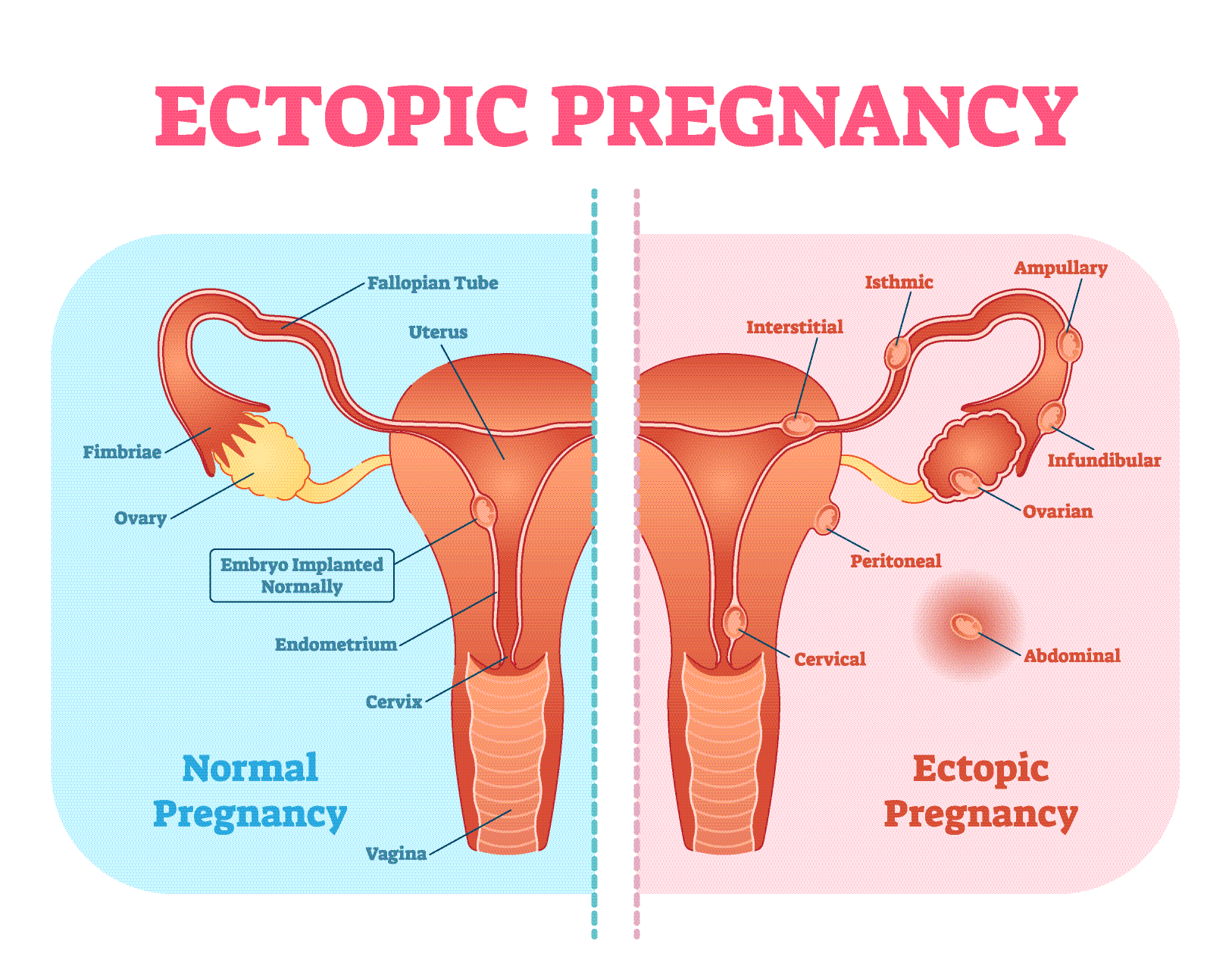
In an ectopic pregnancy, the egg implants itself in an area outside of the uterus that is not able to support the growth it goes through.
The egg travels to the wrong area during the journey it is supposed to take down the fallopian tubes to the uterus to imbed itself into the lining wall where it can develop.
Types of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies most commonly take place in the fallopian tubes. These are called tubal pregnancies and will lead to the fallopian tubes bursting open. The ruptured tube will lead to life-threatening bleeding if it is not treated.
Other types of ectopic pregnancies may also occur. These include the non-tubal ectopic pregnancy in which the egg implants and grows in the ovary, abdominal cavity, or cervix.
Heterotopic pregnancy is another type of ectopic pregnancy wherein one fertilized egg implants itself outside the uterus while the other implants and grows outside.
What Are the Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Tubal and Non-tubal Pregnancy
All tubal and non-tubal ectopic pregnancies have the same symptoms at the start of the pregnancy as any safe pregnancy. These include:
- Missed period
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness or weakness
It is very possible for no signs of an ectopic pregnancy to be present and for it to still be detected during a routine pregnancy scanning.
However, it is still likely that between the 4th and 12th week of pregnancy, an individual may show some symptoms. These include:
- Vaginal bleeding and brown-colored vaginal discharge
- Belly pain
- Pain on one side of your body
- Sharp abdominal cramps
- Pain in the shoulder or neck
These symptoms mostly depend on where the blood collects and which nerves are irritated.
In the situation where the fallopian tube ruptures there can also be severe bleeding and pain. The rupture can show itself using other bodily signs as well, such as urging a bowel movement, sharp shoulder pain, severe dizziness, and pale skin.
Heterotopic Pregnancy
On the other hand, if the ectopic pregnancy is a heterotopic one then, due to its painful nature, it will be discovered in the initial stages of the pregnancy.
There is also a likelihood that after the removal of the ectopic pregnancy if the levels of the hormone hCG continue to rise, the pregnancy in the womb may still be able to continue.
What Can be Done to Prevent Ectopic Pregnancy
Unfortunately, there is not much that can be done to prevent ectopic pregnancies specifically. Anyone can have an ectopic pregnancy.
However, certain risk factors can be taken into account that may increase the chances of having an ectopic pregnancy. These include:
- Having a previous ectopic pregnancy
- Having any sexually transmitted disease such as Chlamydia, which can cause inflammation of the fallopian tubes and other nearby organs, increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy
- Taking fertility treatments
- Having any surgery for the fallopian tubes
- Using an IUD or Tubal ligation as a birth control
- Smoking before trying to get pregnant
How is an Ectopic Pregnancy Treated
After carefully monitoring the condition of the patient, depending on the situation, doctors will advise one of the following two treatments:
- Medication
- Surgery
The medication procedure will involve an injection of methotrexate which will stop the pregnancy from growing any further.
The surgery procedure will involve a laparoscopy being performed to remove the fertilized egg, at times with the affected fallopian tubes.
How to Deal with the Aftermath of Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is an incredibly difficult situation to go through, both physically and mentally. The individuals involved must take time to grieve no matter how long it is.
It is also equally important that professional help is taken if the grief becomes too difficult to handle. This will only help things to get better faster and more effectively.
If someone wants to try for pregnancy again after going through an ectopic pregnancy they should consult a medical professional and take the appropriate time to wait according to the particular procedure they took. This prevents the next fetus from being negatively affected by the treatment.
If someone does become pregnant after an ectopic pregnancy then scans of the pregnancy should be taken early on to ensure that everything is alright.
Conclusion
As it can be seen, an ectopic pregnancy is a high-risk situation that should be dealt with urgently. However, if someone wants to get pregnant again after the removal, they can for sure do so, but make sure to consult with medical professionals first. Even though the chances of having another ectopic pregnancy do increase, the risk is still low.